As of January 26, recent Nipah virus infection cases have emerged in West Bengal, eastern India, with five confirmed cases reported and nearly 100 people quarantined, including one patient in critical condition. In response, neighboring countries like Thailand and Nepal have intensified epidemic prevention measures, enhancing testing at airports and border ports to curb potential spread.
Amid this urgent public health crisis, BGI Group, a global leader in genomics and biotechnology, steps forward with cutting-edge solutions to enhance surveillance, detection, and containment, drawing on decades of experience in pandemic response.
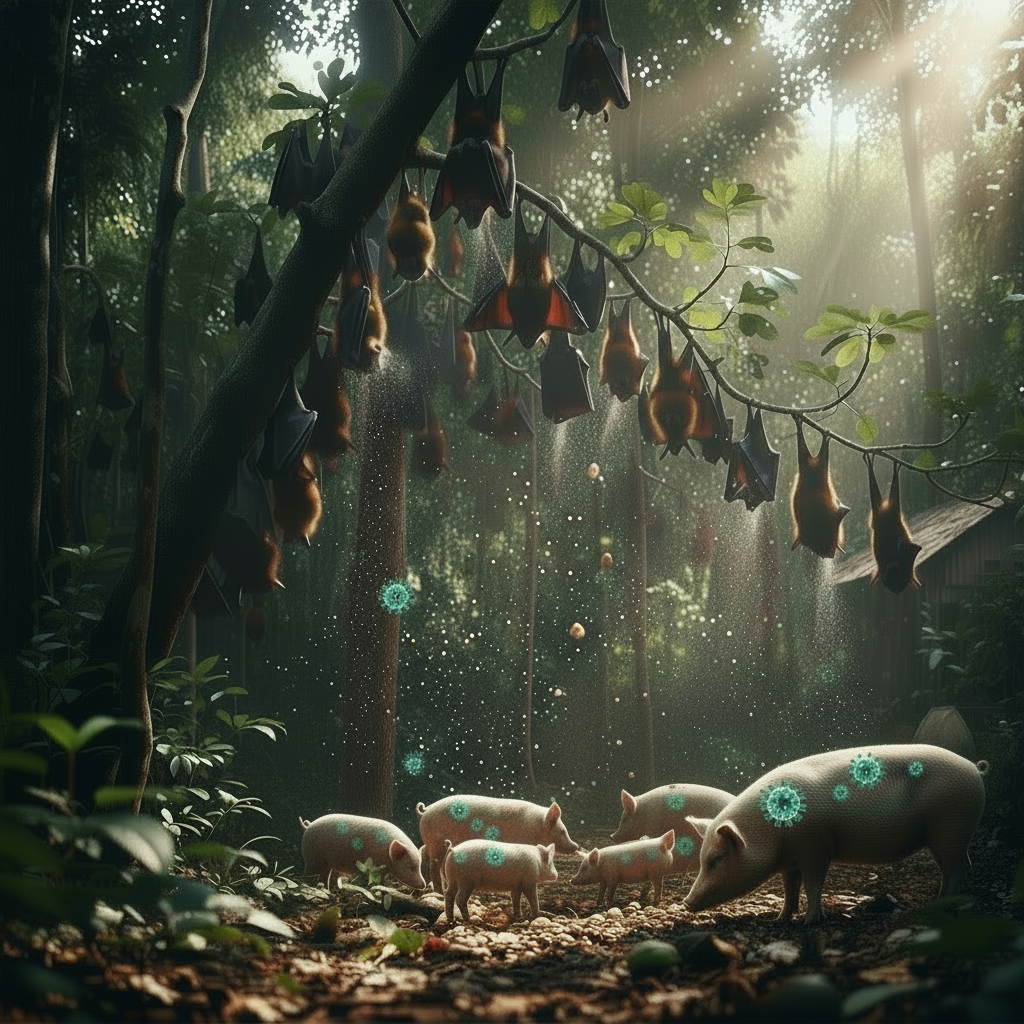 Nipah virus infection, a zoonotic illness in South and Southeast Asia, spreads from fruit bats to animals like pigs. Human infections stem from direct contact with infected animals' fluids (blood, urine, saliva), contaminated food such as bat-tainted fruits or date palm juice, or close contact with patients' secretions in family or healthcare settings. (AI Generated Image.)
Nipah virus infection, a zoonotic illness in South and Southeast Asia, spreads from fruit bats to animals like pigs. Human infections stem from direct contact with infected animals' fluids (blood, urine, saliva), contaminated food such as bat-tainted fruits or date palm juice, or close contact with patients' secretions in family or healthcare settings. (AI Generated Image.)
Nipah, a henipavirus first identified in 1999 during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia, has since triggered nearly annual outbreaks in Bangladesh since 2001 and periodic cases in eastern India, with reports also in the Philippines and Singapore.
This zoonotic illness primarily occurs in South and Southeast Asia, jumping from natural reservoirs like fruit bats to humans and animals, including pigs, causing significant economic losses for farmers.
Human infections stem from direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids (blood, urine, saliva); consumption of contaminated food, such as fruits or raw date palm juice tainted by bat secretions; or close contact with infected patients' fluids, including nasal secretions, urine, or blood—often in family or healthcare settings.
 Essential precautions to prevent Nipah Virus infection. (Source: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India)
Essential precautions to prevent Nipah Virus infection. (Source: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India)
Symptoms range from asymptomatic cases to acute respiratory infection, fever, headaches, myalgia, vomiting, and sore throat, progressing to dizziness, altered consciousness, seizures, encephalitis, and coma within 24-48 hours. The incubation period is typically 4-14 days, though up to 45 days has been reported. While most recover fully, some suffer residual neurological issues or relapses.
The case fatality rate of Nipah virus infection is estimated at 40–75% but can vary by outbreak depending on surveillance and clinical management in affected areas.
Leveraging decades of expertise in pandemic outbreak surveillance, monitoring, and testing, BGI Group offers a robust suite of solutions tailored to combat the Nipah virus, addressing the critical gaps in detection and intervention.
BGI’s metagenomics sequencing technology, built on its proprietary platforms with independent intellectual property, stands as a cornerstone. This advanced system allows for the simultaneous detection of over 36,000 pathogens in a single test, making it invaluable for identifying Nipah virus amid complex infections or in regions with multiple endemic diseases. By analyzing genetic material directly from samples, it differentiates Nipah from similar viruses, providing insights into viral mutations and transmission dynamics.
Paired with BGI SIRO AI-Powered Localized Solution for High-Throughput Genetic Testing platform, this creates a streamlined "sample-in, report-out" process that delivers results in as little as 10 hours. This rapid turnaround is crucial in outbreak hotspots, enabling healthcare providers to isolate cases swiftly, trace contacts, and implement containment measures before the virus spreads through communities or healthcare facilities.
Complementing this, BGI's Nipah Virus Nucleic Acid Detection Kit, developed on its established nucleic acid technology platform, utilizes PCR-fluorescent probe methods for highly specific amplification of targeted viral genomic regions. Designed for operational simplicity, it requires minimal training, boasts exceptional sensitivity to detect low viral loads and ensures a short turnaround time.
 BGI’s Nipah Virus Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (PCR-Fluorescent Probe Method).
BGI’s Nipah Virus Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (PCR-Fluorescent Probe Method).
In 2020, the kit was rigorously calibrated by China's National Institutes for Food and Drug Control for emerging infectious diseases, including Nipah, validating its stability and reliability. This not only supports clinical laboratories in confirming infections but also aids public health efforts by facilitating large-scale screening during outbreaks, securing precious time for epidemic control.
The Nipah virus's high lethality demands proactive solutions, and BGI Group stands ready to safeguard communities. By harnessing these innovations, we can turn the tide against this infectious disease.
Source:
WHO: Nipah virus infection
https://www.who.int/health-topics/nipah-virus-infection#tab=tab_1
The Independent: What is Nipah virus? Symptoms to watch out for as India races to contain deadly outbreak
https://www.independent.co.uk/asia/india/nipah-virus-outbreak-symptoms-signs-india-b2906226.html



